Diabetes is a serious threat to global health that respects neither socioeconomic status nor national boundaries. The latest data published in the International Diabetes Federation shows that 463 million adults are currently living with diabetes. Without sufficient action to address the pandemic, 578 million people will have diabetes by 2030 and that number will jump to 700 million by 2045.
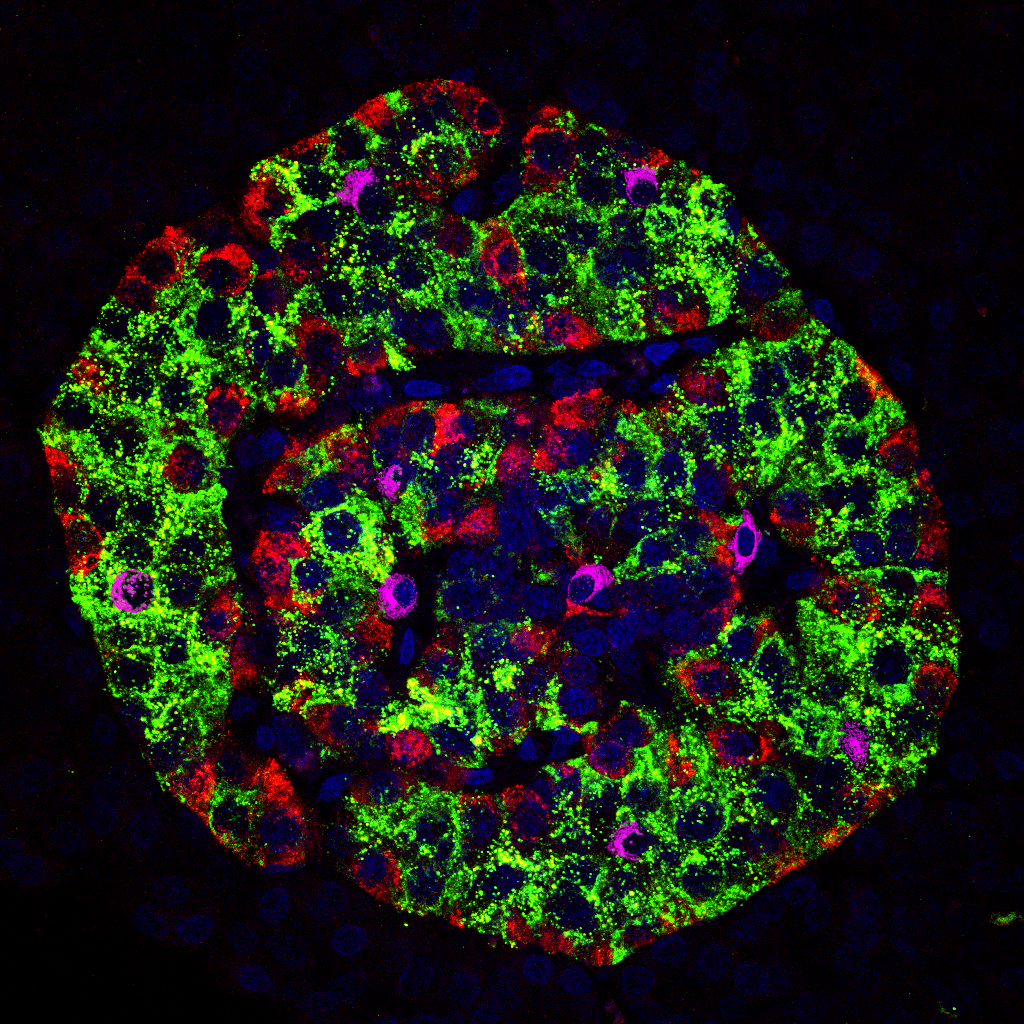
The main researches area of DiabInnov is in metabolic diseases, diabetes and islet biology using human islets, clinical samples as well as animal models of obesity and diabetes.
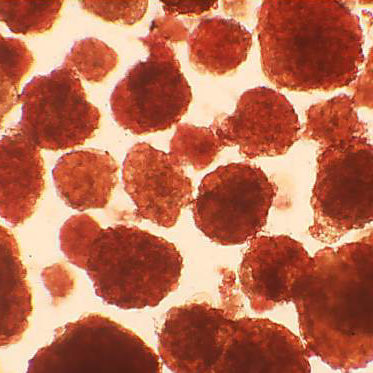
The majority of our research is focused on human islet isolation for clinical transplantation and translational research, complemented by fundamental research on human islet cell biology.


Our research team aims also to identify and validate new molecular biomarkers associated with obesity and its comorbidities, in particular type 2 diabetes. Therefore, we created ABOS BioBank (Biological Atlas of Severe Obesity), a collection of metabolic tissues (liver, muscle, visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, intestine) and blood samples (plasma, serum, DNA) collected as part of a clinical trial on more than 1600 patients with Body Mass Index (BMI) ≥ 35 kg / m2 who underwent bariatric surgery.
Moreover, our researchers have extensive experience with large animal models, in particular the pig model, which shows a great translational value, and has provided important tools and insight into digestive diseases research. The pig model represents a relevant model to test the efficacy of innovative medical devices and accelerate their transfer to clinical application.